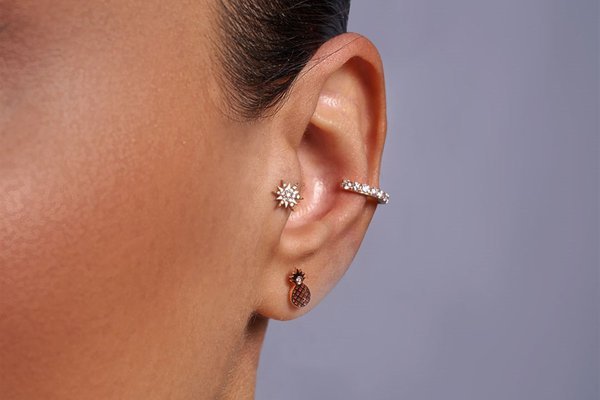
Tragus piercing
A tragus piercing is a piercing that is located on the small piece of cartilage that covers the ear canal.
In this way it is one type of cartilage piercing, opposed to the traditional position for earrings, lobe piercings that are located on the fleshy part of the ear. Under the skin the outer one third of the canal is cartilage and inner two thirds is bone. Usually a puncture is performed in one ear. However, there are people who pierce the tragus on both sides. Tragus can be called a good place for puncture because of the large number of available jewerly. In the piercing of the tragus are worn standard earrings, chain-studs, labrets etc. Usually the diameter of the hole is 1-1.6 mm.
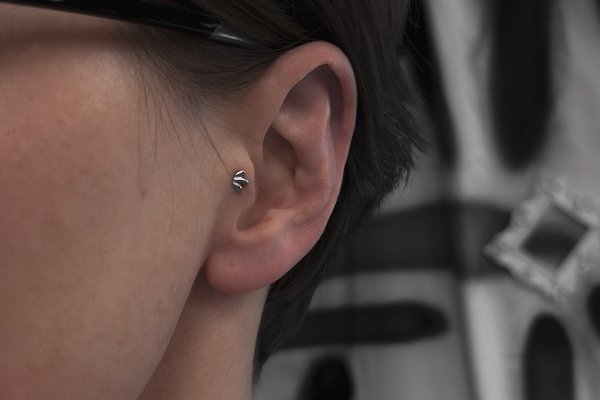

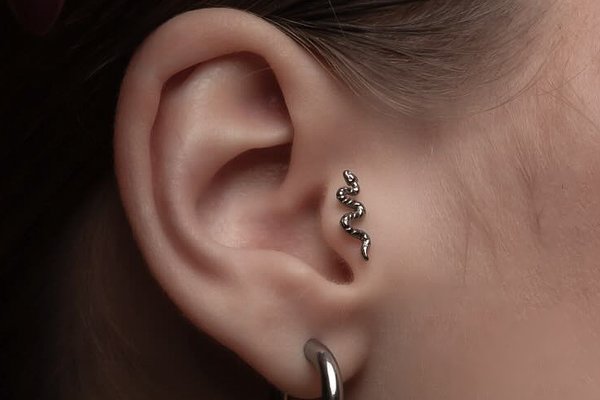
Types and benefits
The standard puncture is made in the direction of the front back with an exit towards the ear canal.
The type of body modification is a vertical tragus. In this case, the barbell is inserted vertically through the skin in the area of the trugus. The original version is a double trugus piercing. Reasons to choose a tragus piercing:
Aesthetic look.
- An opportunity to become like celebrities. Trugus puncture made by movie and music stars - Scarlett Johansson, Zoe Kravitz, Rihanna.
- Ability to change different jewerly - rings, labrets and studs.
- Reduced pain during the procedure. There are few nerve endings in the tragus, which reduces the severity of pain and discomfort.
- Reduced risk of bleeding. Cartilage has few blood vessels. The puncture does not usually bleed or bleed slightly.
It is believed that puncturing a tragus helps to get rid of a chronic migraine. The effect is achieved by influencing the biologically active zone on the principle of acupuncture. The disadvantage of this type of puncture is the possible difficulties of self-insertion a earring or a labret. Due to the thick cartilage in this part of the ear, the puncture heals within 3-6 months.
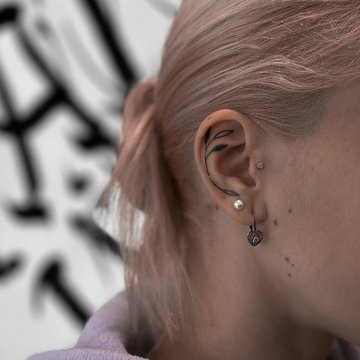

An experienced master performs a tragus piercing in 15-20 minutes.
Before the session the piercer will clarify what kind of puncture you want to do, will help you choose the jewerly. Treatment of the ear with an antiseptic solution is a mandatory step of the procedure. The master works in gloves, which reduces the risk of infection. The next step is to mark the location of the puncture with a special marker. Piercer will show you the mark in the mirror so you can be sure of the correct location. In most cases, people puncture the central part of the tragus. At this stage, you can adjust the position of the future piercing. The procedure is performed with a sterile needle. Before insertion, the jewerly is treated with an antiseptic solution.
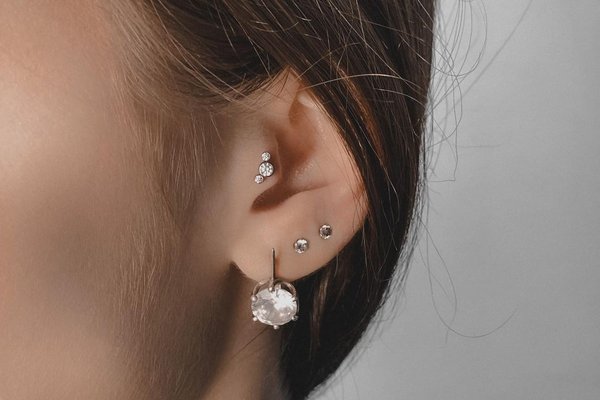
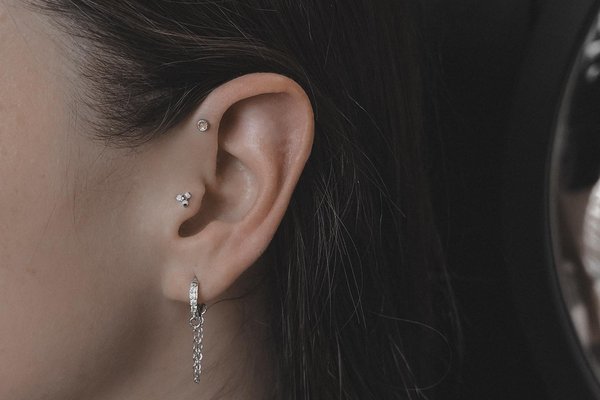


The procedure lasts no more than half an hour. However, in the next 3-6 months it is necessary to care for the puncture hole to avoid the development of inflammatory process.
Cartilage tissue regenerates more slowly than skin, so the healing period lasts longer. The first 3-5 days after the procedure puncture can cause discomfort. You can feel pain at the slightest touch. The jewerly is easy to touch during hair or face washing.
The absence of pain and the impression that the wound has healed can be deceptive. Piercers recommend to perform daily treatment of the tragus for at least 3 months. Aftercare procedure:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- Treat the skin around the tragus with the solution recommended by the master.
- Wash off the contamination - the remains of dried blood and crusts.
- Gently move the labrette forward and backward.
- With a cotton swab clean the surface of the rod on both sides.
- Wipe and clean the dirt hole thoroughly.
- Gently move the jewerly back and forth to get the antiseptic solution inside the hole. If you are wearing a ring, rotate it gently in both directions.
If the ear is wet after treatment, you need to wet the surface with a dry napkin. Pirsers do not recommend changing the jewerly for at least 3 months before full healing of the puncture. Replacement decoration earlier can cause irritation and infection of the wound.

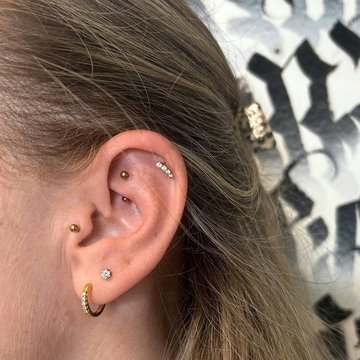

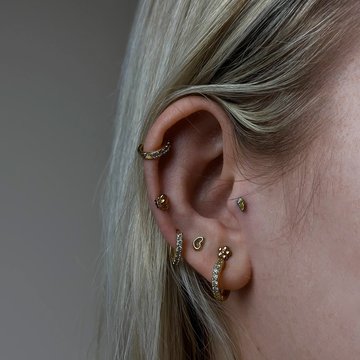
Common decoration - rods and studs, labrets, standard rings and rings with balls.
The labret is a rod with a flat disc on one end and a twisting ball on the other. The length of the rod is usually 8-10 mm. The diameter of the ball is 3-5 mm. Labrets are easy to remove if it is necessary. This is a good option if you like to change jewerly often.
An earring is a piece of jewelry attached to the ear via a piercing in the earlobe or another external part of the ear. The rings are often fitted with a clips or screw backing. If the backing is flat after closing, the ring can rotate in puncture by 360°. The popular rings sizes for the tragus piercing are 6-10 mm in diameter. Self-insertion of the ring with the ball can be difficult.
Masters recommend choosing jewelry made of titanium, medical steel or gold. These materials are biologically compatible with living tissue and hypoallergenic. Chemical inertia is another important advantage. Titanium, steel and gold ornaments do not oxidize when interacting with air, cosmetics and detergents.
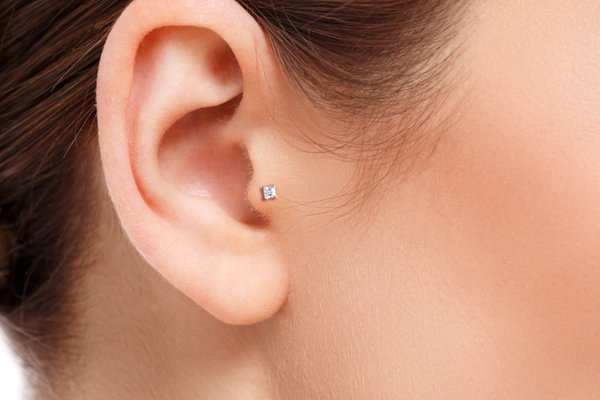
To remove the labret, you need to press the back flat part to push the rod forward.
To remove the labret, you need to press the back flat part to push the rod forward. Then you need to unscrew the fixing ball. After you have removed the ball, push the rod back so that you can grab it by hand from the back of the puncture. Gently pull out the rod.
If you feel pain, as well as in case of inflammation of the puncture hole, do not independently remove the jewerly. Contact your master and follow his/her recommendations. Signs of infection:
- Pus discharge from the wound.
- Skin redness.
- Swelling of surrounding soft tissue.
- Pulsation in the area of tragus piercing.
- Burning sensation and itching.
In the presence of these signs should immediately contact a piercer or doctor.
Soft tissue seal around the puncture site:
In some cases, near the site of the puncture appears a seal, which is a keloid scar. Scar tissue is formed at the site of traumatic damage to cartilage and skin. Keloid scar is usually not harmful to health. In the case of psychological discomfort caused by a non-aesthetic type of compaction, it can be removed surgically.




 Create a sketch in the VEAN TATTOO AI generator
Create a sketch in the VEAN TATTOO AI generator




